Is Magnesium a Good Conductor of Electricity?
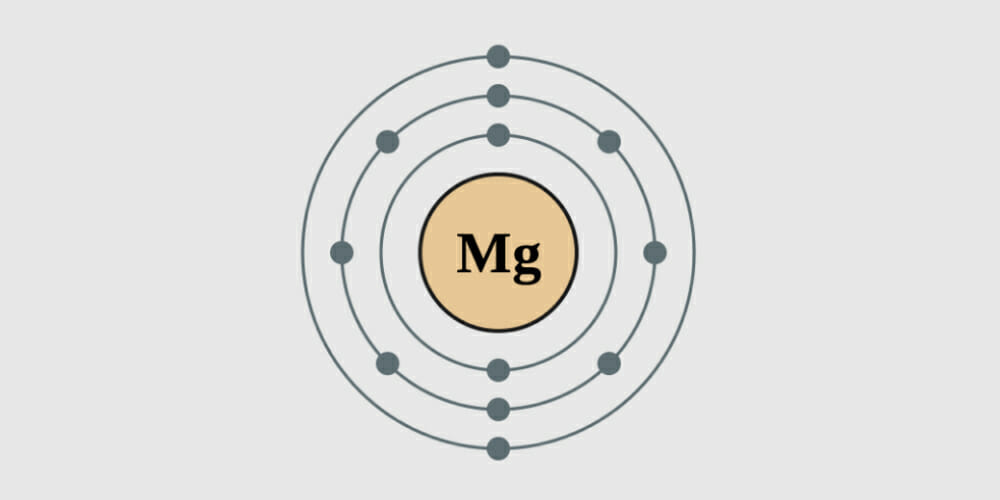
Does magnesium conduct electrical current? And if so, in what state (aqueous or solid)? Being an electrician with a bit of an interest in chemistry, I can easily explain the conductivity of Magnesium in detail.
With two electrons in its valence shell, magnesium belongs to the group 2 family in the periodic table, and the s-subshell can only hold two electrons. The electrons in the metal can’t conduct when the subshell is full. Since its subshell is filled, no electrons can move, yet it conducts electrical current. The electrical conductivity of the group two family is an intriguing concept in electrochemistry that you should know. Let’s unravel this conundrum.
Quick Summary: S-P hybridization is a unique characteristic that all group 2 metals (such as beryllium, magnesium, and calcium) share. The metal can now reach the empty states in the p-subshell since their s- and p- electron subshells overlap. Because of this, magnesium can conduct electricity, as can all group 2 metals.
Let’s go deeper.
Magnesium: Is It a Conductor or An Insulator?
Heat and electricity cannot pass through an insulator but may go through conductors.
Because magnesium permits the movement of heat and electricity, like all other metals, magnesium functions as a conductor, as it is typically found in ionic form, it has poor conducting qualities.
Magnesium Conducts Electricity in What Way?

Due to the movement of electric flux that creates the electric current, a metal can conduct electricity. Let’s talk about the electrical conductivity of magnesium.
Only when magnesium is combined with or dissolved in an aqueous liquid can it transmit electricity. When the magnesium’s valence electrons receive the necessary energy to excite them in a higher energy orbit or energy state, they dissociate, creating an electric flux and current flow.
Electrical Conductivity of Mg
The current density per unit length of the conductor, expressed in Siemens per meter, is a measure of the electrical conductivity of a substance.
As for Magnesium:
It has a 0.226106/cm ohm electrical conductivity. The magnesium’s characteristic governs how quickly current passes through it. Magnesium’s resistivity and conductivity are inversely correlated with one another.
Is Magnesium a Reliable Electrical Conductor?
If the substance is a metal and permits current to flow, it is an excellent conductor of electricity. Let’s talk about whether or not magnesium is a good conductor.
Magnesium is very reactive with oxygen, nitrogen, and even carbon dioxide, which lessens its conducting properties and makes it a poor conductor of electricity compared to other metals. As a result, it is thought to be unsuitable for electrical conduction.
Comparing the Electrical Conductivity of Mg and Cu (Copper)
If there is less overall electric flux flow through the metal’s cross-section area, it is a poor conductor. Now let’s discuss why Mg is a worse conductor than Cu.
Due to the ease with which electrons separate from copper compared to magnesium, copper is a better conductor than magnesium. Due to the extensive electron resistance from the copper atom’s atomic core, which is significantly smaller than the magnesium atom, the valence electrons can readily overcome the electrostatic force.
Magnesium has two electrons in the valence shell, whereas copper has an atomic number of 29 and a valence electron of 1. Simple electron separation from the metal is possible.
Structure and Bonding of Mg
A metal’s valence shell’s overall number of electrons determines its structure and bonding.
- Mg has an atomic number of 12 and a hexagonal close-packed structure.
- Mg has a covalent radius of over 140 pm.
- Mg creates ionic and covalent bonds.
- Magnesium reacts with atmospheric oxygen gas to form various oxides.
Take a look at some of our related articles below.
- Does mercury conduct electricity
- Does sulfuric acid conduct electricity
- Does isopropyl alcohol conduct electricity
Video Reference
chemistNATE
