How to Test Air Fuel Ratio Sensor with Multimeter
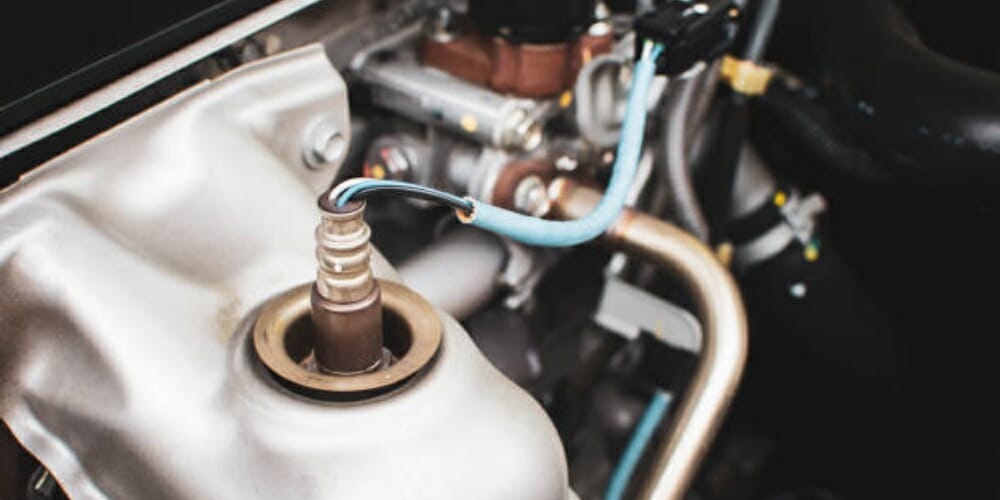

The car’s air-fuel ratio sensor, commonly known as the O2 or lambda sensor, measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust and communicates it to the ECU. This data is used to optimize the air-fuel ratio engine in the combustion chamber. Its primary function is to reduce the amount of dangerous gas emitted into the environment by detecting the amount of unburned oxygen departing the system.
In general, to test an air-fuel oxygen sensor using a multimeter, first put it in resistance mode and then examine the heating element. Connect your test leads to the heater power and ground connection pins or wires. Take a look at the oxygen sensor’s multimeter reading.
The oxygen sensor can get rusted and requires testing to ensure appropriate operation. This article will help you learn how to test an air-fuel ratio sensor with a multimeter.
What Does an Air Fuel Ratio Sensor Do?

The O2 sensor is a compact, straightforward device with a tip sensor installed in the exhaust pipe. As a result, the sensor is intended to monitor the oxygen ratio in exhaust emissions. The oxygen ratio measured by the sensor is subsequently related in real-time to the ECU, which regulates the fuel and oxygen ratio required.
The air-fuel ratio sensor is mounted before the catalytic converter in the exhaust manifold or the front exhaust pipe. It is also known as the ‘front O2 sensor.’ The air-fuel ratio sensor must detect the amount of oxygen in the exhaust and send input to the engine computer (PCM). The computer changes the air-to-fuel ratio based on the air-fuel ratio sensor data to keep it at the optimal level, around 14.7:1, or 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel.
How to Test the Air Fuel Ratio Sensor with a Multimeter
When attempting to test an oxygen sensor, it is usually a good idea to be aware of the type of oxygen sensor installed in your vehicle. The most popular ones have one to five wires connecting them to the rest of the car, and it’s a good idea to identify the kind before you start testing it.

Method 1: Signal Wire Test
Step 1: Check that the car’s engine is adequately cooled.
Step 2: Set the Digital MultiMeter to voltmeter mode.
Step 3: Back probe the oxygen sensor’s signal voltage and ground wire.
Step 4: Connect the Digital MultiMeter’s black lead to the back probing ground signal cable.
Step 5: Connect the Digital Multimeter’s red lead to the signal voltage wire.

Step 6: Turn on the car’s engine.
Step 7: If your car’s sensor wires function correctly, the voltmeter should register between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
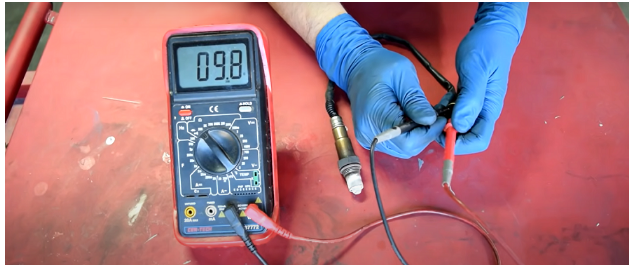
If you don’t get readings like those given above, you should have your car’s oxygen sensor examined and fixed or replaced by a mechanic. It is critical for the correct air-fuel ratio engine in the combustion chamber.

Method 2: Heater Wire Test
Step 1: Check to see whether the engine is turned off.
Step 2: Set the digital Multimeter to Ohmmeter mode.
Step 3: The next step is to back-probe the hot and ground wires of the oxygen sensor heater.
Step 4: Connect the multimeter’s red lead to the hot wire and the black lead to the heater ground wire with the Multimeter.
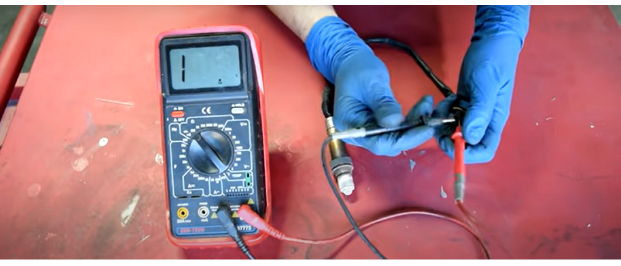
Step 5: The next stage is to determine whether you have suitable sensors, which will be evident if the Multimeter values are between 10 and 20 ohms.
How to Know if the Air Fuel Ratio is Bad
Let’s talk about how to spot a damaged oxygen sensor; let’s go over the obvious indicators of o2 failure. Though getting to the O2 is difficult owing to its physical position, there are certain warning signs to tell you if there is a problem. The obvious signs are as follows:
- The exhaust pipe emits a foul odor.
- A reduction in gas mileage.
- The check engine light illuminates automatically.
- The idling of the engine is harsh.
- When starting the automobile, the starter becomes difficult.
The presence of the check engine light, in conjunction with any other symptoms listed above, may indicate a defective air-fuel oxygen sensor. To diagnose the issue, examine the diagnostic trouble code contained in the Engine Control Unit. Consider further tests if the identified issue code suggests the o2 is failing.
Wrapping Up
After running the various tests, you should be able to establish whether the issue is with the sensor or another component. If the O2 has a problem, you may immediately resolve it. If you are unsure, take your vehicle to a competent technician. Remember that detecting and correcting a problem immediately prevents you from developing more serious problems. I hope I answered your questions about testing the air-fuel ratio sensor with a multimeter.
References
Website Resources:
