How to Test 3 Wire Coil On Plug with Multimeter (3 Ways)

Coil-On-Plug (COP) ignition systems are the norm for most car models but testing one for issues can get confusing, so below I will explain how, using a multimeter.
If you’re working on this kind of Direct Ignition System, you must know how they operate, specifically how to test them. By doing so, you’ll be prepared to respond if your ignition system experiences a malfunction. You can check the health of your Coil-On-Plug ignition coil using various tools, and one of the most reliable is the digital multimeter.
In general, you can use a multimeter to check your three-wire Coil-On-Plug ignition coil through:
- Testing the Power Circuit
- Testing the Ground Circuit
- Testing the Triggering Signal Circuit
Read on for my step-by-step methods.
3 Ways to Test the 3 Wire Coil On Plug with a Multimeter
When testing a 3-wire Coil-On-Plug ignition coil, you should first test for spark through a spark tester.
Remove the ignition coil, spark plug, and spark plug wire out of its position. Attach the spark tester to ignition coils and connect it to the battery’s negative terminal.
Then, have an assistant crank the engine. If there is a spark, then your ignition coil is good. However, if there’s no spark to the ignition coils, there’s something wrong with them.
Then, to determine the actual cause of a no-spark result for each ignition coil, run these multimeter tests:
Power Circuit Test
So, after confirming that there’s no spark, you need to check if each ignition coil is receiving 10 to 12 Volts DC. With that, test the power circuit with these steps:
Step 1: Remove the ignition coil from its electrical connector.
Step 2: Set the multimeter’s mode to VOLTS DC.

Step 3: Probe the multimeter’s red test lead to that ignition coil’s power circuit.
Step 4: Connect the multimeter’s black test lead to the battery’s negative (-) terminal.
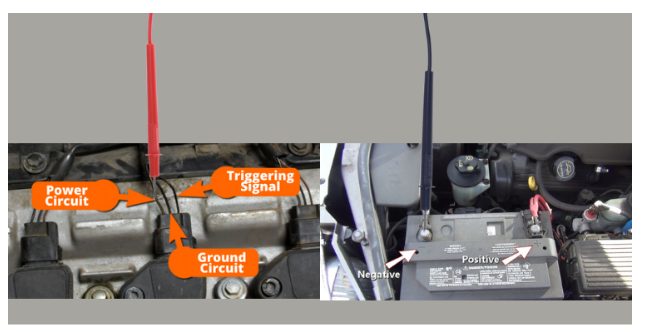
Step 5: Have your assistant turn the key to its ON position.
Step 6: Read the result.
Possible Results:
The power circuit has 10-12 volts
- It means your power circuit is good. You can then move forward to the ground circuit test.
One ignition coil didn’t show 10-12 volts
- With that, you have just ruled out the Coil-On-Plug ignition coil as the cause of the problem because it cannot operate without 12 volts. Since the new ignition coil won’t spark without electricity, replacing it will waste time and money.
- In most Coil-On-Plug ignition systems, the power circuit is shared by all of the coils. In that case, the most likely reason for this missing voltage is a damaged ignition coil connector or an open circuit issue in the wire connecting the connector to the engine wiring harness. After fixing the short, conduct a spark test to ensure the ignition coil is now functioning.
All ignition coils have no power or don’t show 10-12 volts
- This indicates that the voltage is supplied by a relay or fuse that has blown or failed. So, you need to find the fuse and relay’s location and determine whether a replacement is required. With that, refer to the wiring diagrams in your repair manual.
- Then after changing the faulty relay or blown fuse, test the ignition coils again.
Ground Circuit Test
Next, make sure the ignition coil is receiving ground. Here are the steps:
Follow Steps 1 & 2 from the previous method:
(Remove that ignition coil from its electrical connector. Set the multimeter’s mode to VOLTS DC)
Step 3: Probe the multimeter’s black test lead to that ignition coil’s ground circuit.
Step 4: Connect the multimeter’s red test lead to the battery’s positive (+) terminal.
Step 5: Have your assistant turn the key to its ON position.
Step 6: Get the result.
Possible Results:
The ground circuit has 10-12 volts
- The ground circuit is in good condition if the multimeter displays 10-12 Volts. Now you may proceed with the triggering signal test.
One ignition coil lacks ground
- The Coil-On-Plug ignition coil cannot function without this ground, so you have just ruled out that ignition coil as the problem’s root cause.
- It is a waste of time and money to replace the ignition coil because the new one won’t spark if the Ground is absent. In most Coil-On-Plug ignition systems, all the coils share the ground circuit. With that, an open circuit in the ground circuit is most likely the issue of your ignition coil.
- After correcting the short, perform a spark test to confirm the ignition coil is now operational.
No ignition coils have ground
- It is a highly uncommon occurrence that typically results from human error.
- Typically, this Ground was not reattached after replacing the engine. Using a jumper wire, you can ground this circuit. You can jumper wire one Coil-On-Plug ignition coil to the Ground, providing Ground to all the others.
- So, crank the vehicle while this jumper wire is connected to the ground.
- The jumper wire to the Ground should start the car, or at the very least cause the ignition coil to ignite if the Ground circuit has an open circuit issue.
- Fix the open-circuit problem, then restart the car or test for a spark again.
Triggering Signal Test
After ensuring that your ignition coil receives 12 volts, ground, and no sparks, the next test is to ensure that the fuel injection computer is sending the Triggering signal to the ignition coil (that isn’t sparking).
For this test, you require a digital multimeter with the ability to read the Hertz frequency. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Switch the multimeter to Hertz (Hz) more. (1)
Step 2: Reattach the ignition coil to the electrical connector.
Step 3: Using a suitable tool to pierce the wire or back-probe the connector, probe the multimeter’s black test lead to the triggering signal wire.
Step 4: Connect the multimeter’s red test lead to the battery’s positive (+) terminal.
Step 5: Turn the key to start the engine.
Step 6: Get the result.
Possible Results:
The multimeter test read 30 to 60 Hertz (Hz)
- This test result is accurate and verifies the existence of the Triggering signal. The Coil-On-Plug ignition coil itself is defective and must be replaced.
One ignition coil has NO signal
- In that case, the most frequent cause is the trigger signal circuit of that particular coil open. The positive news is that the cause of the issue has now been determined not to be the COP ignition coil itself. It won’t work to replace the Coil-On-Plug ignition coil with a new one since the new one won’t spark without the Triggering signal.
There is no signal on any ignition coils
- The most common reason is that the crankshaft position sensor is malfunctioning. Another reason is a problem with the ECM (fuel injection computer). It does occur; however, it is pretty uncommon.
- So, additional tests are necessary to determine if the crankshaft position sensor or the ECM is at fault.
Bad Ignition Coil Symptoms
A defective ignition coil prevents your engine from starting. It’s the primary cause of your engine’s poor performance. The following are bad ignition coil symptoms:
Power Reduction
A defective ignition coil will cause the car to operate uneventfully. In addition, idle time will cause your vehicle to lose power and sound or feel rough. It might not stall and finally accelerate slowly.
Check Engine Light will Illuminate
Due to variations in every car, an inefficient ignition coil may register a different code for the issue. As a result, you will see a code for an engine misfire.
Gas Mileage is Deteriorating
An ineffective ignition coil will occasionally fail or not work to its full specs. Even though your vehicle appears to be operating normally, decreased gas mileage is a solid sign that something is amiss.
Difficulty Starting
If the spark plug isn’t receiving enough power through its spark plug wire, you’ll have difficulty starting your car. Any ignition coil arrangement can experience it, but engines with a single ignition coil are more prone to experience it.
Suddenly Backfires
An audible bang is produced by the engine backfiring when unburned fuel unexpectedly escapes from the exhaust fuel. If you don’t fix a damaged ignition coil immediately, it could cause severe engine damage.
Misfiring Engine
When you stop, a defective ignition coil will cause your engine to run rough, tremble, or vibrate. Additionally, a sputtering sensation is caused by the engine’s misfiring when traveling at regular speeds.(2)
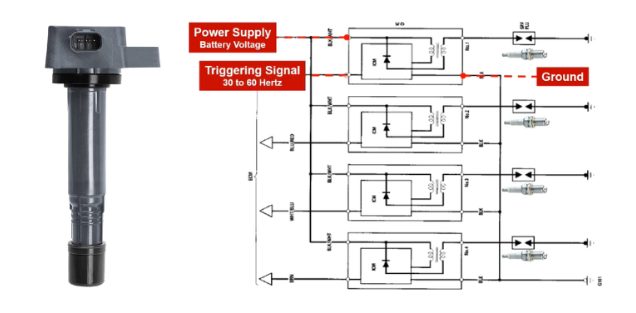
Understanding the Three Coil-On-Plug Wires
The 3-wire Coil-On-Plug ignition system contains three circuits. If any of these inputs are absent, the ignition system will not spark. The three circuits are as follows:
Power Circuit
The power circuit, which is one of the coil-on-plug wires, is the one that supplies the coil with 12 volts. The Coil-On-Plug ignition coils are often all fed by the same fuse or relay.
Ground Circuit
Another significant difference between the 3-wire Coil-On-Plug ignition coil is its full-time Ground circuit. No ignition control module interrupts (opens) this circuit, unlike in a typical ignition coil.
There is no “full-time” Ground circuit in the conventional distributor-type ignition coils and the two-wire in the connector Coil-On-Plug ignition coils. It is because the ignition module, whether or not it is integrated into the ECM, may regulate this Ground circuit by turning it ON and OFF.
Moreover, the ignition coil includes the ignition module, and this cable serves as the “full-time” ground for the transistor (ignition module).
Triggering Signal Circuit
One of the critical characteristics of the 3-wire Coil-On-Plug ignition system is that it receives Triggering signals instead of any Switching signals. The triggering signal instructs the transistor when exactly to cause the ignition coil to spark.
Take a look at some of our related articles below.
- How to test ignition coil with multimeter
- How to wire an ignition coil diagram
- How to test ignition control module with multimeter
References
(1) hertz – https://www.britannica.com/science/hertz
(2) engine’s misfiring – https://www.jdpower.com/cars/shopping-guides/what-happens-when-a-car-misfires
Video References
Hammond Auto LLC
Automotive Diagnosis: Cars Repair &Training Guides