Can a Battery Drain with the Negative Cable Disconnected?

What effect would disconnecting the negative cable from a vehicle’s battery have on it? Would it cause the battery to drain? Why do people do it? What else causes battery drain?
Key Takeaways: A battery can drain with the negative cable disconnected from it, but it will drain at a lower self-discharge rate (~1-15%) than if left connected (~20%), and the vehicle is unused for a long period.
As batteries age, their performance characteristics can change, but how quickly and in what ways depend on many variables.
Here’s a rough idea, but take these with a grain of salt:
| Month | Self-discharge Rate (%) | Discharge (Ah) | Discharge per Day (Ah/day) | Discharge per Hour (Ah/hour) | Approx. Battery Age (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.0167 | 0.0007 | New to 1 year |
| 1 | 2 | 1.0 | 0.0333 | 0.0014 | 1-2 years |
| 1 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.05 | 0.0021 | 2-3 years |
| 1 | 5 | 2.5 | 0.0833 | 0.0035 | 3-4 years |
| 1 | 10 | 5.0 | 0.1667 | 0.0069 | 4-5 years (or more) |
| 1 | 15 | 7.5 | 0.25 | 0.0104 | 5+ years (near end of life) |
I will go into more detail below.
Effects of a Disconnected Negative Cable
Let’s briefly consider what would happen if the negative cable was disconnected or no proper ground point was created (while the car was being used).
In this situation, the circuit would not be complete, so the vehicle could not provide a continuous and uninterrupted flow of electricity, which is necessary for the vehicle’s electronics to function normally.
Consequently, the current would try to create an alternative return path to the battery ground. The resulting disruption or diversion from the normal flow would create a host of electrical problems, such as:
- damage to sensors and coils
- electronic glitches
- engine misfires
- flickering headlights
- heavy cranking
- low alternator voltage
- relay problems
- weakened spark plugs
- wrong signals
It can also affect the battery and make it unable to start the vehicle. As you can see, it can cause severe damage that may require costly repairs.
Impact of Disconnecting the Negative Cable on the Battery
Although a disconnected negative cable might not drain the battery much, it can cause it not to charge properly and the vehicle to fail to start.
We’ve assumed that the battery is healthy and the negative cable is simply disconnected. But, a weak battery, even if capable of showing full charge, can drain rapidly, whether connected or not. If you suspect a weak battery, monitor its voltage level and conduct a load test to confirm.
If it’s an old battery nearing the end of its expected lifetime, now would be a good time to replace it anyway.
Why Would You Disconnect the Negative Cable?
Disconnecting only the negative battery cable on a car is often done for safety reasons. Here are some of the key reasons:
- Prevent Short Circuits: If you’re using a metal wrench to disconnect the battery and it accidentally touches any part of the vehicle body, it won’t create a short circuit if you disconnect the negative cable. But if you disconnect the positive cable and the wrench touches any metal part of the car, it creates a short circuit. Since the car frame/body is typically connected to the negative terminal of the battery (the car is “grounded” to the negative terminal), touching the frame with a tool connected to the positive terminal could potentially cause a dangerous electrical event.
- Avoid Electrical Damage: Accidental short circuits can not only pose a safety risk, but they can also damage sensitive electronic components in your car. Modern cars are full of electronics, and a short circuit could cause expensive damage.
- Reduce Fire Risk: A spark in the wrong place (like near spilled fuel or oil) could cause a fire. Disconnecting the negative terminal first and connecting it last reduces the likelihood of a spark occurring.
- Personal Safety: A direct short can cause the battery to explode, spraying acid and other materials in all directions, potentially causing injury. By disconnecting the negative cable first, you reduce the risk of creating a short and, thus, the risk of an explosion.
Disc disconnecting the negative cable first (and reconnecting it last) is all about safety and preventing damage to your car.
Disconnecting the Negative Cable

Some vehicle owners deliberately disconnect the negative cable for certain reasons.
The usual reasons for disconnecting the negative cable from the battery are:
- Protecting the battery when leaving the car parked for a long period;
- Testing the alternator (simple test);
- Testing for battery drain.
Protecting the Battery
Everything connected to a vehicle’s battery will drain the battery over time.
So, if leaving the car parked for a long period, disconnecting the negative cable is one way to prevent too much drain. This way, you may only lose about 5-15% monthly charge compared to 20% if the negative cable was connected.
In other words, disconnecting the negative cable protects the battery from self-discharging too much by reducing the self-discharge rate. The difference might seem small but can be significant if the vehicle is parked for several weeks or months.
The actual rate of self-discharge depends on the following factors:
- The battery’s capacity, age, condition, number of charge/discharge cycles it has undergone, and the extent of sulfation inside.
- The ambient temperature around the battery.
Alternatively, if you’re not going to use the vehicle for a long time, at least start the car once a week or fortnight and let the engine run for a few minutes. Another option is to connect the battery to a battery maintainer or float charger, adding a little charge at intervals to keep it topped up without overcharging.
Also, disconnect unnecessary accessories that put an extra load on the battery.
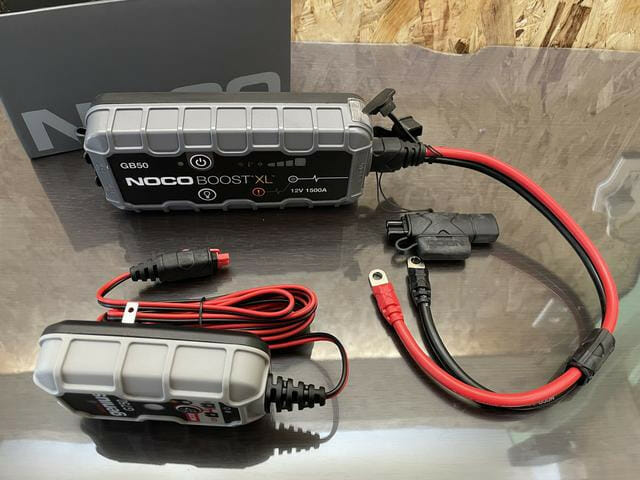

Testing the Alternator
A simple test to check the alternator involves disconnecting the black cable from the battery’s negative terminal.
As safety precautions, park the car away from flammable materials, trees, and other structures; wear heat-resistant gloves to protect yourself from a hot engine and potential sparks; and don’t disconnect the red cable from the battery’s positive terminal while the engine is running, as it could cause serious damage to the ECU and other electrical components.
Follow these two steps to test the alternator:
- Start the engine as normal and keep it running. If the engine was already running, turn it off and let it cool down for a while before running it again.
- While the engine is running, remove the black cable from the battery’s negative terminal (NOT the red one from the positive terminal).

A good alternator will keep the engine running even after you disconnect from the battery’s negative terminal.
If the engine stops, stalls or its performance degrades, it’s likely that the alternator is faulty. However, it’s possible that the alternator barely produces enough energy even while the engine appears to be running normally.
Causes of Battery Drain
A disconnected negative cable or poor ground point is not the only cause of battery drain.
Besides the negative cable, ground point, and battery, three other components can cause high battery drain: a bad alternator, starter, and high-powered accessories. Otherwise, anything connected to the battery can potentially drain it over a certain amount of time.
A Bad Alternator
A bad alternator can undercharge, overcharge, or completely drain an otherwise healthy battery within half an hour.
It will be unable to charge the battery adequately, and a damaged one will probably not be able to charge it. Intermittent charging also harms the car’s battery, as the engine will keep shifting for its power source.
Consequently, you may only be able to continue driving as far as the battery’s remaining charge allows with a bad alternator. When the battery’s voltage drops below approximately 12.5 volts, it will no longer be charging, and the car will eventually halt.
Besides checking the alternator for possible worn-out brushes, check for a loose or tight belt and dust or oil accumulated on the alternator.
A Bad Starter
A bad electric starter can drain a battery, especially if you keep trying to start the car multiple times.
It normally draws a current of 90-200A for 5-10 seconds when starting. It might be bad due to a short circuit in the solenoid, a high current draw, a faulty ignition switch, an oil leak, or some other reason.
You can check whether a bad starter is the cause by first eliminating the battery or doing a “percussive maintenance” test:
- You eliminate the battery by disconnecting the cables from the battery (negative first), reconnecting them, and turning on the lights. The starter might be the problem if the lights are brighter than before.
- You do a percussive maintenance test by lightly tapping the starter to see if this makes it work again. If it does, the starter is the problem, and the fix is temporary.
Accessories
Some vehicle accessories require more power and battery drain than others, especially if left on by mistake while the car is parked.
You can check whether an accessory is causing the battery to drain by disconnecting the suspect accessory, typically a high-powered one, and seeing if it makes a difference.
If left on by mistake, you can expect the battery to keep powering it for a few hours before it drains too much that it would be unable to start the car. This assumes the battery is in good and healthy condition with a full charge. For example, headlights may last around 2 to 3 hours; hazard lights around 3 to 5 hours and the radio 4 to 6 hours.
The Purpose of the Negative Cable
A vehicle’s negative (black or brown) cable is typically the ground cable.
It provides a ground connection for vehicles and is necessary to complete the circuit because their electrical circuits are closed-loop systems. It ensures all the vehicle’s electronics can function normally.
Ground Point
The negative cable is connected to a bare metal (non-painted) spot on the vehicle’s chassis or engine, which becomes the ground point.
By grounding, we normally use the car’s chassis (metal body or frame) as part of the circuit, as it helps to reduce the cable length and simplify the layout. The car’s frame joined to the negative terminal becomes the ground, and the car’s polarity is called “negative earth” [Hillier & Thornes, 2012].
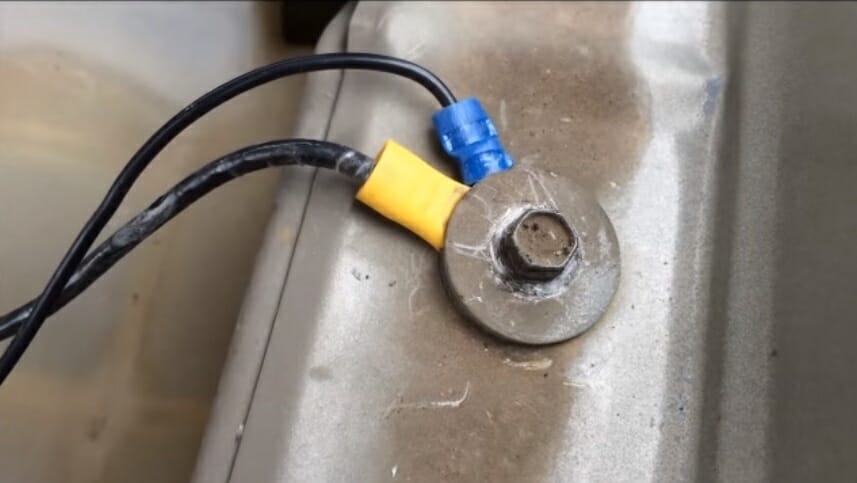

Whichever ground point is chosen, it must be clean, secure, rust-free, corrosion-free, and have low resistance (below 0.2 volts).
Electrical Flow
The ground point is a conductor between the battery’s positive and negative terminals.
The circuit is only complete when both battery terminals are connected with a load in between. The pressure difference generates an EMF (electromotive force) to drive the electrical current. The current flows from the battery’s positive (+) terminal to its negative (-) terminal.
All the vehicle’s electronics are connected to and rely on this loop. A continuous and uninterrupted flow of electricity is essential for them to function normally.
Ground Return System
When connecting a battery to an electrical circuit, the negative (grounded) wire serves as the “earth” or “return”, whereas the positive one is the “supply.”
The return is so-called because it indicates a circuit’s (conventional) current flow. The substitution of the vehicle’s body for the return cable forms the “ground return” system (see diagram below).
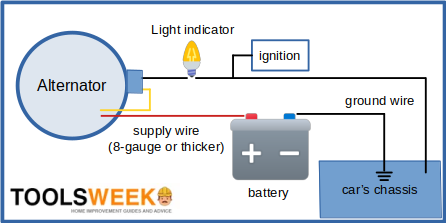
An alternative is possible, called an “insulated return,” but it’s usually only arranged for petrol tankers, as they transport highly flammable content.
Testing the Battery Drain
If you’re still worried about battery drain, you can use a multimeter to test exactly how much the battery drains.
Step 1: Turn Off All Components
Turn off all electrical components in the vehicle and remove the key from the ignition.
Step 2: Check the Battery’s Voltage
Set a multimeter to measure DC volts and attach probes across the battery’s two terminals.
Attach the red probe to its positive (+) terminal and the black probe to its negative (-) terminal. The reading should show 12.4-12.6 volts when fully charged.
Step 3: Disconnect the Negative Cable
Disconnect (only) the black cable from the battery’s negative terminal, leaving the red cable still connected.
Step 4: Measure the Current
Set the multimeter to measure the current in mA. Connect its black wire to the COM port and the red one to the highest amp input.
Attach the red probe to the battery’s negative terminal and the black one to its positive terminal. A reading of 20-50 mA would be acceptable, but a reading higher than 50 mA would indicate a high drain.
You will need to investigate what is draining the battery that much by investigating all connected components individually. You don’t have to connect the probes to the components. Keep them on the battery’s terminals and remove each fuse while taking separate current readings.
Preventing High Drain on the Battery
To prevent a high drain on the battery:
- Ensure the starter and alternator are in good working condition.
- Ensure no unnecessary accessories are left on by mistake.
- Disconnect the negative cable if leaving the car unused for a long time, or use a battery maintainer or float charger.
References
Battery maintainer. https://www.goo-net.com/pit/shop/0208665/blog/323569.
V. A. W. Hillier & Nelson Thornes. Hillier’s fundamentals of motor vehicle technology. Book 1, Sixth Edition. Nelson Thornes Ltd. 2012.
Video Reference
Fix My Car
