What is a Neutral Wire (Wiring Basics)
What if I told you that one of the unsung heroes of our electrical systems is a simple wire—specifically, the neutral wire?
Often overlooked in the face of its ‘hot’ counterparts, the neutral wire plays an indispensable role in our day-to-day lives, providing a safe path for electrical current and keeping our devices humming along smoothly.
But what exactly is a neutral wire? How does it work, and why is it so vital to our daily lives? In this article, we will untangle the mystery of the neutral wire and highlight its crucial role in our electrical systems.
What Exactly is a Neutral Wire?
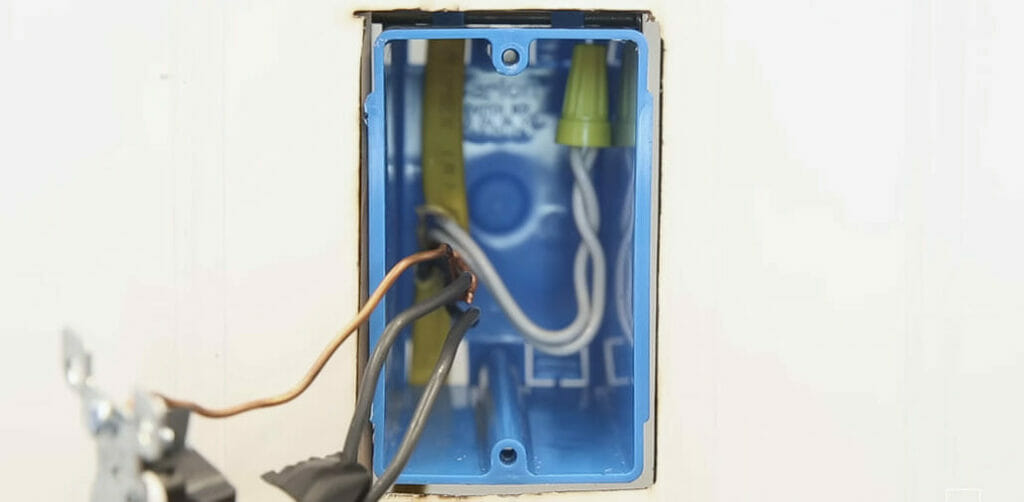

The neutral wire, typically white or gray in the U.S., is essential to our electrical systems. It’s distinct from the ‘hot’ wires, usually colored black or red, which carry electricity from the power source to your appliances.
In simple terms, the neutral wire forms the return path for the electrical current.
Once electricity has passed through a device—a lightbulb, a TV, or your refrigerator—it needs a way back to the power source to complete the circuit. That’s the job of the neutral wire.
This wire is termed “neutral” because it’s at a voltage close to or at zero under normal conditions.
This neutral voltage makes it safer than the ‘hot’ wires, but it can still carry current if the circuit is active or there’s a fault in the system.
So, to sum up, the neutral wire is a critical player in maintaining safe and effective electrical systems by providing a return path for the electrical current.
Without it, the circuit would be incomplete, and electricity would not flow.
A Deep Dive into the Neutral Wire’s Role

To better understand the role of the neutral wire, it helps to think of an electrical circuit like a circular race track. The ‘hot’ wire is the starting point, supplying the electricity that speeds into your appliances.
The electricity does its job, powering your device, but then it needs a way back to the source to complete the circuit—just like a race car returning to the starting line. This is where the neutral wire steps in.
Electricity needs a complete path to flow in every alternating current (AC) circuit, like in most residential and commercial buildings. As mentioned, the neutral wire provides the return path.
Without it, the current supplied by the hot wire would have nowhere to go once it powered your device.
This would lead to an accumulation of electrical charge, causing overheating and potentially dangerous situations like electrical fires.
The neutral wire also helps maintain voltage stability in your electrical systems. Every device or appliance in your home is designed to operate at a specific voltage.
By providing a return path for the current, the neutral wire helps ensure that the voltage levels remain within safe operating ranges for each device.
Another important point to note is the potential of the neutral wire. Under normal conditions, it’s at or near zero volts relative to the earth’s ground, meaning there’s no voltage difference between it and the ground.
This ‘neutral’ state minimizes the risk of electrical shock if a person touches the neutral wire. However, remember it can still be dangerous to touch if a fault or the circuit is loaded.
In summary, the neutral wire serves two crucial roles in our electrical systems: it completes the electrical circuit, provides a path for the current to return to its source, and helps maintain voltage stability.
Without the neutral wire, our electrical systems would be inefficient and potentially hazardous.
Neutral Wires Across Different Applications

The neutral wire’s role stretches across every electrical application in our homes and workplaces, providing a vital service in ensuring the functionality of our devices.
Let’s explore some specific applications to understand better how neutral wires influence our daily lives.
| Application | Role of the Neutral Wire |
|---|---|
| Home Electrical Systems | Forms the backbone of the system by ensuring a return path for the current from each outlet, light fixture, and appliance back to the main panel and utility grid. |
| Appliances | Present in every plug or cord of appliances like refrigerators, microwaves, washing machines, and TVs. Provides a way for the current to flow back to the power source, enabling safe operation. |
| Lighting Systems | Used in every lighting fixture, from simple bedside lamps to elaborate chandeliers. Works alongside the ‘hot’ wire to complete the circuit and enable electricity flow. |
| Power Tools | Part of the power cord in each power tool, such as drills, saws, or sanders. Provides a safe path for the returning current, ensuring safe operation. |
As such, the neutral wire is omnipresent in all electrical systems. Regardless of the device’s complexity, it will require a neutral wire if it uses AC power.
References
Organizations:
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). www.ieee.org
- National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA). www.necanet.org
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). www.iec.ch
- National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA). www.nema.org
Video Reference
Leviton
