How Many Amps for 10-Gauge Wire?
Generally, a 10-gauge (AWG) copper wire is good for handling up to 30 amps in most cases, depending on its insulation, whether it is encased in a conduit, the wire’s length, and the ambient temperature. It should be treated as the maximum, whereas around 24 amps should be considered the safer normal current capacity for continuous use.
Read more about the ampacity of a 10-gauge wire and the considerations, including the length of the wire.
A 10-Gauge Wire
A 10-gauge AWG wire has a diameter of 0.101900” (2.58826 mm), a circular mil area of 10,383.311783 mm, and is equivalent in other wire size systems to 12 SWG and BWG.
Considerations
Type of Wire
Copper wire has very low resistivity, enabling it to handle higher currents more easily than aluminum wire.
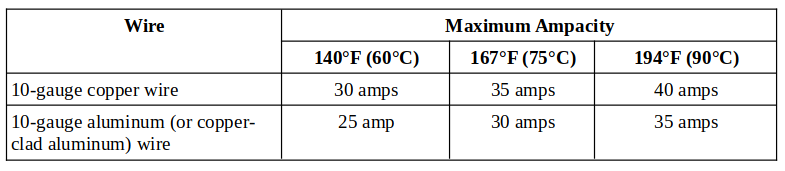
The limit of 24 (safe) to 30 (max.) amps applies to copper wire up to 140°F (60°C). These limits are less for aluminum (or copper-clad aluminum) wire (20 to 25 amps, respectively). Refer to the table below.
Length of Wire
If you consider the wire’s length, a 10-gauge copper wire 10 meters long would have a resistance of around 0.032 ohms.
A 10-gauge wire should be acceptable for appliances within 55 feet of the main breaker panel for a voltage drop not exceeding 3% in a 110V system. For a 240V system, the length can be doubled. But if you need to wire over a longer distance, consider the voltage drop the appliance can tolerate.
Applications
A 10-gauge wire is normally used for air conditioners, electric laundry dryers, and other appliances that need up to 30 amps.
They usually also require a 4-prong plug. A 10-gauge wire would not be adequate if connecting, for example, an electric stove, which would need an 8/3 wire instead. Only in controlled outdoor or industrial situations can a 10-gauge wire be used for a little higher current than 30 amps.
In other uses, 10-gauge wire is specified for up to 55 amps for chassis wiring and 15 amps for power transmission.
Use of a Conduit
A conduit would lower the ampacity rating depending on its size and what other wires run alongside it. In free air, a wire can potentially handle more without overheating. Regardless, a 10-gauge wire should be on a 30-amp circuit breaker.
Circuit Breaker and Maximum Load
A 30-amp circuit breaker or fuse must protect a 10-gauge wire.
This requirement holds regardless of whether it is a 10/2 or 10/3 cable, but the voltages and wattages would differ. The maximum wattage load is 2,880 watts for a 120V system and 5,760 watts for 240V. Refer to the table below.
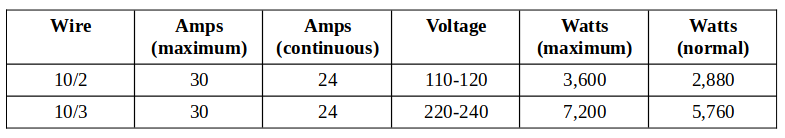
However, the current should not constantly exceed 80% of the 30 amps, which is 24 amps.
This means that although a 10-gauge wire can handle up to 30 amps (for a load of 3,600 or 7,200 W), this should be treated as the maximum, whereas around 24 amps (and 2,880 or 5,760 W) should be considered the safer normal current capacity for continuous use.

