What Does FLO Mean on a Battery Charger?

If you’re confused about a “FLO” code displaying on your new smart car battery charger, this article explains what it means.
It’s not an error code, although it might seem like one. It is short for a specific way to charge the car battery that only comes on under certain conditions.

Key Takeaway: The FLO code on a battery charger means float charging, i.e., maintaining a constant voltage to keep the battery’s voltage topped up after it is fully or almost fully charged. So, it’s an operational code that tells you in what manner the battery is now being charged.
I also go through how float charging is useful when applying it and how to deal with related issues detected by car battery chargers while charging below.
Float Charging
Float charging is usually indicated by “FLO” displayed on the battery charger.

It indicates that the battery charger is charging the battery in float charge mode, i.e., float charging it.
It means that the battery is 100% or almost fully charged, but the charger is now maintaining a constant voltage to keep the battery’s voltage up. It doesn’t let the voltage drop below the full level, as in trickle charging. It monitors the battery and only charges it as necessary to ensure it remains at full capacity.
The unit will stay in float charge mode if the charger is connected to the battery and plugged into a functioning AC outlet.

Individually, the charger maintains a voltage of a little over 2 volts in each cell, which comes to approximately 12.5-12.8 volts for a 6-cell 12-volt battery. Also, it keeps the battery fully charged without overcharging it and boiling its electrolyte.
The exact voltage might range between 12.4 and 12.8 volts (while the engine is off).

Float charging differs from normal charging:
- Normal Charging: The charger supplies current to the battery continuously to increase its state of charge and voltage. A battery that is discharged or has a low charge is normally charged this way. The voltage supplied is irrespective of the discharge rate.
- Float Charging: The charger only supplies current to the battery when fully charged, and its state of charge or voltage drops to ensure it remains fully charged. The voltage supplied is proportional to the discharge rate.
Benefits of Float Charging
Float charging ensures the battery is kept fully charged.
Without float charging, the battery self-discharges, and it will discharge further if it’s used. Although the self-discharge rate is minor, it can be significant if the battery is charged fully, unused, or stored for a long time. You might think the battery is still fully charged when using it after a long time, but it will be less than full.
A lithium-ion battery can retain most of the charge, even after a few months. But car batteries are typically lead-acid batteries. They self-discharge at approximately 4-6% per month.
So, you might be disappointed if you don’t float or trickle charge a fully charged car battery and think you can use it one month later to start your car!
Suppose you fully charge the battery to 12.8 volts and leave it unused for one month. You might find the voltage somewhere between 12V and 12.3V, which might be insufficient to start the car. You usually need at least 12.4-12.5 volts to crank a vehicle’s engine.
That’s why we use float charging. It helps to maintain the full charge.
How Float Charging Helps
When you float charge a battery, the charger’s battery management system (BMS) does what is necessary at intervals to maintain a full charge.
It prevents the battery from being drained through self-discharge or use. The voltage supplied during float charging is sufficient to keep the battery at full capacity. It, thus, compensates for the discharge.
This is helpful for maintaining a full charge and healthy for the battery. If the battery is left to itself and discharges significantly, it will lead to sulfation, reducing the battery’s lifespan.
Float charging is a saver if you plan to store the battery for several weeks or months. Normally, vehicle drivers (and UPS/Solar-powered system owners) attach their batteries to float/trickle chargers when not used long.
Is Float-Charging Safe?

Float charging is safe for the battery.
You might be concerned about overcharging the battery, but the BMS ensures this doesn’t happen while float-charging. It will not let the battery’s voltage rise above its normal operating voltage. Float charging does not charge beyond the full capacity. It only replenishes the discharged portion.
Rather, float charging helps protect the battery from overcharging, whereas you may have to switch the charger off manually under normal charging at the right time to prevent overcharging.
Float charging is, therefore, a safety feature that avoids overcharging.
Fault Codes when Float Charging
During float charging, you are more likely to come across certain other fault codes than overcharging, but only if something is wrong with the battery, not if the battery is healthy.
The meaning of a specific fault code might differ between chargers, so check the manual for your particular charger. Usually, the fault codes are from FO1 to FO6, and what they indicate is given in the table below.
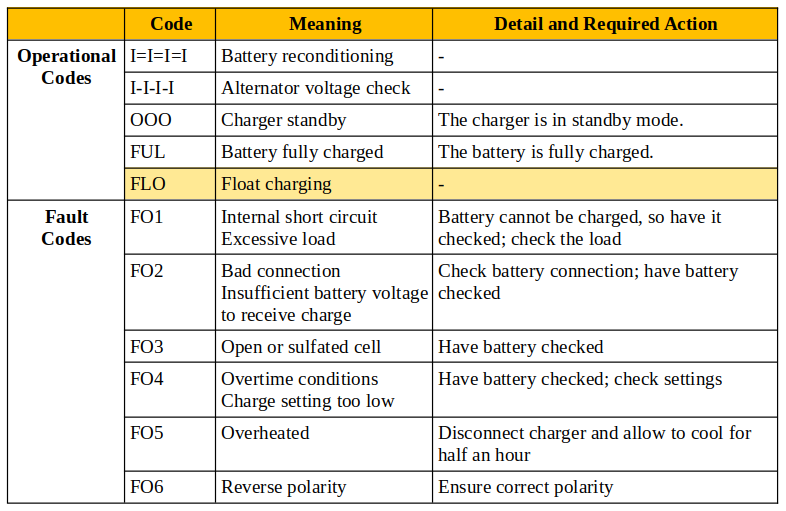
FO1: Internal Short Circuit
A very high-temperature exposure can cause the chemical elements inside to overheat and create an internal short circuit. The cell loses its ability to accept a charge from the charger and will discharge itself until its energy is exhausted.
Don’t ignore a FO1 code. In a worst-case scenario, a short circuit can lead to a fire.

FO1: Excessive Load
FO1 warns that the charger is about to shut down because the current exceeds the safe limit.
A car battery charger requires a certain voltage to charge a car battery properly. The charger will automatically shut off if it detects a high current draw, which is usually due to excessive load on the battery.
FO2: Bad Connection
The connection is bad if the current cannot flow between the battery’s terminals. Due to no current flowing, the charger cannot apply charge between them.
You should check the connections on the battery’s terminals to ensure they are correct and tight.
FO2: Insufficient Voltage
The charger only charges the battery with enough voltage to accept the charge.
A smart charger detects the battery’s voltage level and indicates the amount of charge. It also analyzes whether the battery can accept more charge up to a certain threshold voltage.
This fault code will show if the voltage level is insufficient for the battery to accept more charge.
FO3: Open or Sulfated Cell
The fault code FO3 shows if the battery charger detects an open cell inside the battery.
The battery might be nearing the end of its lifespan, or its lead plates might be physically damaged. The battery cannot be charged because if the charger continues charging, the electrochemical reactions inside could become unstable.
The battery most likely needs replacing.
FO4: Overtime Conditions
An overtime condition occurs when the battery charger has been running for a long period.
Some smart chargers are designed to charge continuously for a fixed interval and will stop charging automatically when that time limit is reached.
FO4: Charge Setting Too Low
Most smart car chargers will alert you if they detect a charge rate set too low.
They continuously monitor the battery’s charge rate. A low charge will take too long and might undercharge the battery. Generally, a low charge rate is generally safer, although it will take longer to fully charge the battery. However, it can increase sulfation on the plates if it’s too low. Avoid sulfation because it reduces a battery’s lifespan.
FO5: Overheated
An overworked battery charger is vulnerable to overheating.
It continuously monitors the temperature through a thermistor. If you see this error code, disconnect the charger and allow it to cool. Around half an hour may be sufficient.
FO6: Reverse Polarity
A smart battery charger can detect reverse polarity.
It analyzes the current passing through the battery’s terminals. It will display the FO6 error code if it detects the current flowing in reverse.

References
Corroded terminals. https://knowhow.napaonline.com/battery-terminal-end-failure-symptoms/
FLO meaning. https://www.stanley12volt.com/_files/ugd/217982_bf3b83560bae40c784b2d1424874457b.pdf
Overheat Protector battery charger. https://www.ebay.co.uk/itm/166051726062
Video References
Style Renegade
V6 News Telugu
