What Ah Means for a Battery (Definition, Ratings, Selection)

Ever wondered what “Ah” means when you’re shopping for batteries? You’re not alone. It’s a term that constantly pops up on battery labels, but many people don’t know what it means.
Key Takeaway: Ah stands for Ampere Hour, a unit of electric charge. It’s a key factor in determining a battery’s capacity or how much power it can supply over some time.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand why Ah is crucial when choosing a battery. Knowing about Ah can help you make a more informed decision. So, let’s get started.
Understanding Ah (Ampere-Hours)

Ah, Ampere Hours is like the battery world’s way of telling you how much “juice” you’ve got. Picture it as a highway for electricity – a higher Ah rating means a wider road, allowing more current to cruise through.
I’ve seen how battery chemistry impacts Ah ratings. For instance, lithium-ion batteries often hold higher Ah ratings than traditional lead-acid ones, which can keep your gear running longer.
Also, don’t forget how the environment plays its part. Cold weather can sap a battery’s strength, reducing its Ah capacity. It’s similar to how your car guzzles more gas in the cold.
So, when looking for the right battery, think beyond Ah. Consider the battery type and where you’ll be using it. It’s about finding the perfect match for your project, just like choosing the right tool for the right job.
Ah Ratings and Their Role in Different Batteries
In my world of DIY and construction, understanding Ah ratings across various battery types is like knowing the right tool for the job. Here’s how they stack up:
| Battery Type | Typical Ah Rating |
|---|---|
| Car Batteries | They’re heavy-duty players, with Ah ratings ranging from 50-80 Ah for smaller ones to over 200 for big guys. |
| Small Device Batteries | Rated in milliamp hours (mAh) |
It’s crucial to ensure you have the right battery for your needs. It’s all about matching the battery’s capabilities with what you’re building.
High vs. Low Ah Ratings

When looking for batteries, whether for my power tools or the latest tech gadget, I always watch the Ah, or Amp-Hour, ratings.
It’s like a battery’s stamina meter, showing how long it can last on a single charge. But it’s more than just a number game—the quality of the battery counts, affecting its longevity and performance under constant use.
A higher Ah means the battery can run longer on a single charge. But it’s not just about the numbers. The real magic lies in the battery’s quality – it determines how well it holds up under constant use.
C Ratings

Now, let’s talk about C ratings, particularly for those heavy-duty deep-cycle and lithium-ion batteries I use in my projects.
This rating is crucial because it indicates how well a battery handles continuous power output. Picture a 1C battery rated at 1Ah – it’s like a reliable workhorse that delivers steady power for an hour without a break.
But here’s a twist: a battery’s chemistry can greatly influence its Ah rating. For instance, lithium-ion batteries usually have higher Ah ratings than traditional lead-acid ones, which means they can run longer.
Plus, external factors like temperature play a big role, too. Extreme cold or heat can impact a battery’s efficiency, similar to how weather conditions affect a construction site.
The Formula for Ah
Here’s a bit of electrical wisdom for you. Do you know the formula P = IV from high school physics? It’s all about power (P) being the product of current (I) and voltage (V). Well, the Ah formula is a neat twist on this.
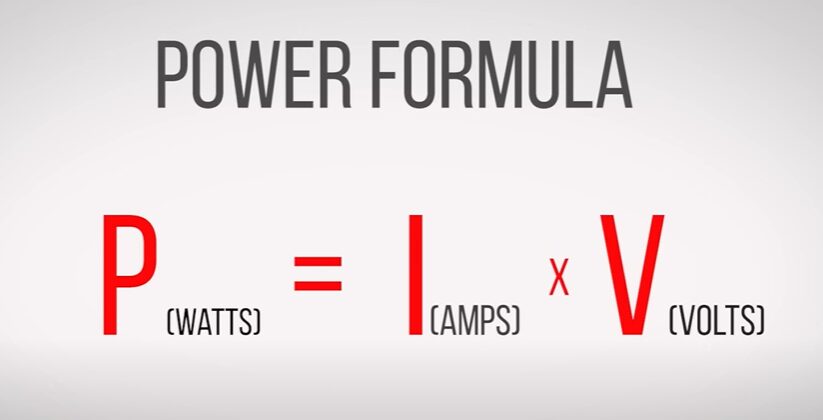
When I’m sizing up a battery for one of my projects, I rearrange it to I = P / V. This tells me the current I need based on the power and voltage. But here’s the kicker: the Ah formula adds a dash of reality by considering how long you’ll use the battery and its efficiency.
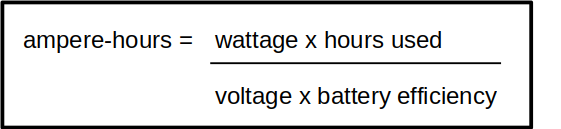
Here’s a pro tip: If you’re unsure about a battery’s efficiency, stick with 0.8. This is a safe bet unless you’re dealing with a brand-new, top-notch battery.
Calculating Battery Capacity
Battery capacity, or its Ah rating, isn’t just a single number pulled from thin air. It’s the sum of all the little parts that make up the battery. Just like when I’m building something, every piece contributes to the whole.
Think of it like a team project. Each cell in the battery adds its bit to the total Ah rating, showing how much your battery packs. The higher the total, the more power you’ve got at your disposal.
So, next time you pick a battery, remember it’s all about teamwork inside that little power pack!
Understanding Battery Specs: Ah vs. Voltage vs. Watt-Hours
When I’m in the middle of a project, picking the right battery is as crucial as choosing the right saw or drill. I don’t just look at the Ah to make the best choice.
Voltage and watt-hours are also key players in this game. Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
| Specification | Ah (Ampere-Hours) | Voltage (V) | Watt-Hours (Wh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| What It Measures | Total charge capacity: how many amps a battery can deliver in one hour. | Electrical potential: the force that drives electrical current. | Energy capacity: how much power the battery can deliver over time. |
| Impact on Performance | Determines the battery’s run time based on the current draw. | Influences the power and speed of the device; higher voltage often means more power. | Provides a complete picture of how long the battery can power a device. |
| Example | A 100 Ah battery can deliver 100 amps for one hour. | A 12V battery can drive a system that requires 12 volts. | A battery with 240 Wh can deliver 20 watts for 12 hours. |
| Usage Consideration | It is essential to understand the duration a battery will last. | The key for device compatibility must match the device’s voltage requirement. | Useful for comparing batteries across different voltages and capacities. |
I remember working on an outdoor lighting project. I had to pick a battery that would last all night. A high Ah was my first thought, but the lights were LED low power.
I needed a balance of Ah and Watt-hours to ensure longevity without overkill. Ultimately, I chose a medium Ah battery with a solid watt-hour rating. It was the perfect match – like finding the right blade for a tricky cut.
References
Organizations:
- PRBA (Portable Rechargeable Battery Association). https://www.prba.org/
- Battery Council International. https://batterycouncil.org/
Books:
- “Practical Electronics for Inventors” by Paul Scherz and Simon Monk. http://instrumentacion.qi.fcen.uba.ar/libro/Scherz.pdf
- “The Art of Electronics” by Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill. https://artofelectronics.net/
Website Resources:
- All About Circuits. https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/
- Electronics Hub. https://www.electronicshub.org/
Video References:
Techquickie
Out of the Woordwork
EXPLORIST life – DIY Campers
cleversolarpower
