What Does Battery Recond Mean? (Deep Dive & Methods)

In a world where we’re constantly looking for ways to be more eco-friendly, battery reconditioning is a hidden gem that many people may not know about.
Battery reconditioning is restoring a battery’s capacity to hold a charge so it works like it’s fresh off the shelf again. This clever technique can save you money and reduce waste by prolonging the life of your batteries, which might otherwise end up in a landfill. What’s even cooler is that it can apply to various battery types, like car batteries, laptop batteries, and even rechargeable AA batteries.
Consider how many devices in your life run on batteries to give you an idea of how useful battery reconditioning can be. You can save some cash, keep your devices running longer, and even help the planet by creating less waste.
Let’s dive further into how this process works and how you can recondition your batteries today!
Why Battery Reconditioning is Important
Understanding why battery reconditioning, or ‘battery recond,’ is important requires looking into the benefits it brings to consumers and the environment. These benefits include extending battery life, saving money, and promoting environmental sustainability.
A. The Benefits of Battery Reconditioning
1. Extending Battery Life: One of the most prominent benefits of battery reconditioning is the potential to extend a battery’s lifespan. Over time, batteries lose their ability to hold a charge due to a build-up of sulfates on the lead plates inside the battery. Battery reconditioning involves removing these sulfates, effectively restoring the battery’s ability to hold a charge. This can give the battery several more years of effective service before replacement.
2. Saving Money: Extending the life of your batteries with reconditioning means you spend less on purchasing new batteries. Whether it’s a car battery, a laptop battery, or a battery for a power tool, a new one can often be costly. By learning to recondition batteries, you can save considerable money over time.
3. Environmentally Friendly: Battery reconditioning is an eco-friendly practice. Each time a battery is disposed of, it poses a risk to the environment due to its lead content and other harmful chemicals. By extending the life of a battery, you reduce waste and limit the need to produce new batteries, which also have a significant environmental footprint.
B. Case Studies or Examples Demonstrating these Benefits
To bring the concept of battery reconditioning into real-world perspective, consider the following examples:
1. Case Study – Fleet Vehicles: Consider a company that operates a large fleet of vehicles. Replacing batteries for these vehicles can become a significant cost. Suppose this company implemented a battery reconditioning program. In a year, they managed to extend the lifespan of their vehicle batteries by an average of 1.5 years. This leads to substantial cost savings, as they avoid the need to purchase new batteries as frequently.
2. Example – Laptop Batteries: Imagine a college student with a laptop whose battery no longer holds charge. Instead of spending money on a new battery, the student learns to recondition it, successfully restoring its capacity. The student saves money and also gains valuable skills in battery maintenance.
3. Environmental Impact: On a larger scale, imagine if 20% of households in a city of 500,000 people learned to recondition batteries and extended the life of just one battery each year. That would mean 100,000 fewer batteries ending up in landfills annually. This highlights the environmental benefit that can be achieved with battery reconditioning.
These examples illustrate how the benefits of battery reconditioning can be realized on both an individual and a larger scale. The importance of understanding and implementing battery reconditioning is clear from cost savings to environmental conservation.
Reconditioning Methods
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of these reconditioning methods can vary depending on the battery’s age, condition, and the specific factors contributing to its degradation.
| No. | Reconditioning Method | Battery Type | Process Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Equalization | Lead-acid batteries | Balancing the battery cells and removing sulfate buildup by applying a controlled overcharge. |
| 2 | Cycling | NiCd and NiMH batteries | Discharging and charging the battery multiple times to restore capacity and break down crystalline formations, improving overall performance. |
| 3 | Chemical Treatment | Lead-acid batteries | Using chemical additives or desulfators to break down sulfate crystals and restore battery performance. Chemical additives are added, and after resting, the battery is recharged. |
| 4 | Balance Charging | Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries | Ensuring equal charge distribution among battery cells using a specialized charger that monitors and balances individual cell voltages during charging. |
| 5 | Refreshing or Conditioning | Various battery types | Discharging the battery completely, often with a specialized device, and then recharging it to remove any memory effect and restore capacity and performance. |
Battery Reconditioning Process
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Step 1. Check the battery’s voltage and ensure it’s at the appropriate level, such as around 12.6V for a standard lead-acid battery.

Step 2. If the voltage is low, proceed to test the battery’s capacity.

Testing the battery’s capacity will help determine how much charge it can store and whether it’s worth attempting the reconditioning process.
Discharge and Recharge
Discharge
Step 1. Connect a resistor or load to drain the battery’s charge safely.
Step 2. Monitor the process closely to prevent the battery from reaching dangerously low voltage levels.
Step 3. Ensure the discharge process is conducted in a well-ventilated area and follow appropriate safety precautions.
Recharge

Step 1. Use a high-quality charger specifically designed for the type of battery being reconditioned.
Step 2. Start the recharge process by connecting the battery to the charger.
Step 3. Set the charger to a low charge rate to promote better battery health and prevent overheating.
Step 4. A slow and steady charge rate is recommended for a more thorough and effective recharge.
Step 5. Monitor the charging process to ensure the battery is not overcharged or exposed to excessive heat.
Chemical Treatment
Step 1. Assessment
- Identify the sulfation issues in the lead-acid battery, characterized by the buildup of lead sulfate crystals.
- Determine if a chemical desulfator treatment is appropriate for the battery.
Step 2. Gather Supplies
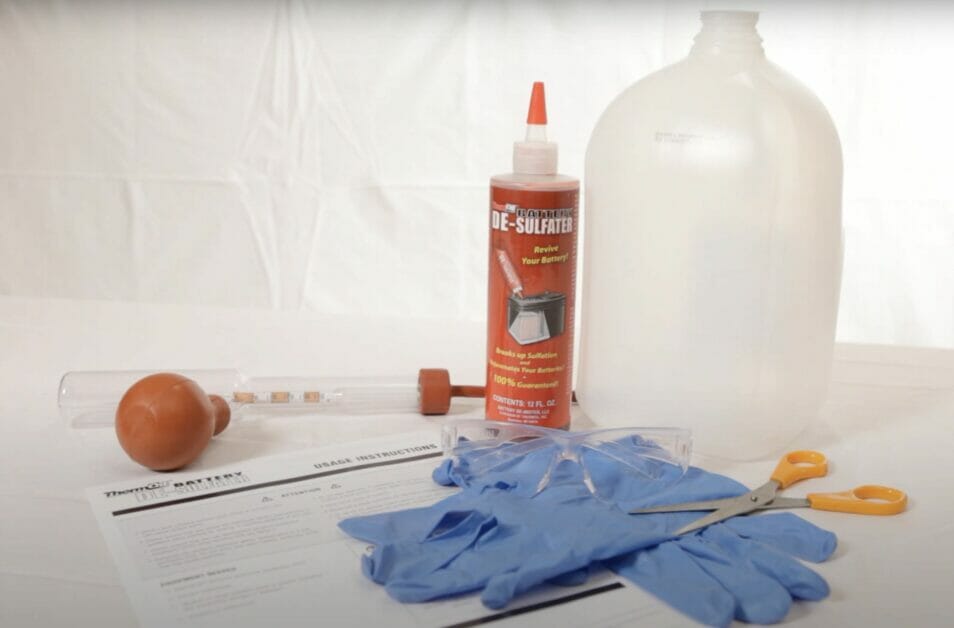

- Acquire a suitable chemical desulfator additive designed for lead-acid battery reconditioning.
- Ensure you have the necessary protective gear for handling chemicals, such as gloves and goggles.
Step 3. Preparation
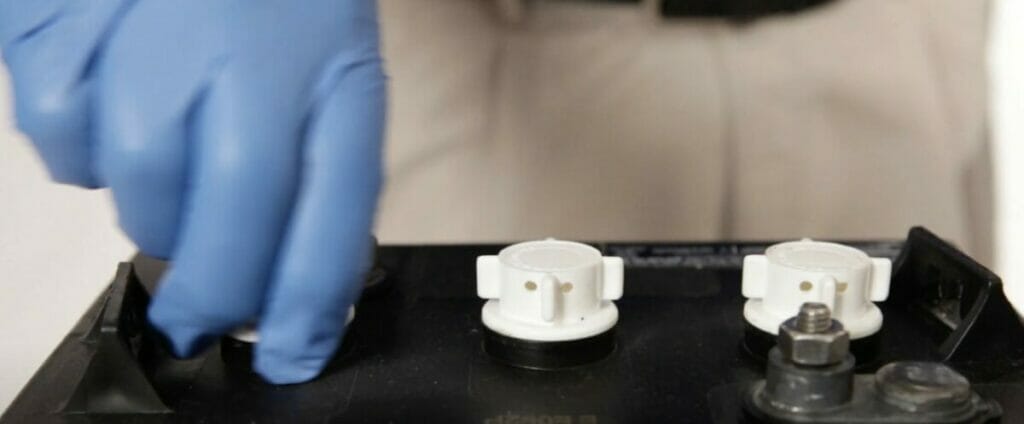

- Carefully remove the battery caps to access the individual cells.
- Confirm that the battery is fully charged or has a sufficient charge level before proceeding.
Step 4. Application of Chemical Desulfator
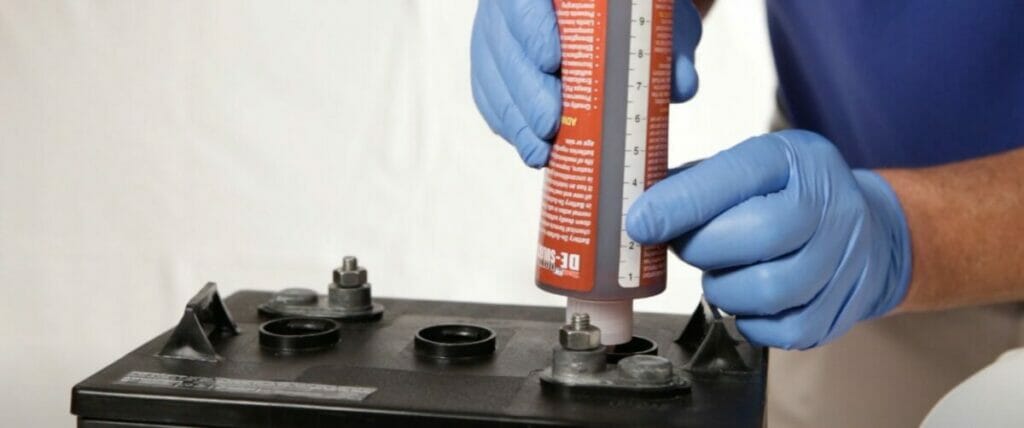

- Follow the instructions provided with the chemical desulfator additive for the appropriate dosage.
- Add the correct amount of the chemical desulfator additive to each battery cell.
Step 5. Mixing
- Gently shake or agitate the battery to thoroughly mix the chemical desulfator additive with the electrolyte solution.
- Be cautious not to spill any electrolyte solution during the mixing process.
Step 6. Resting Period
- Allow the battery to rest for a specific duration recommended by the manufacturer of the chemical desulfator additive. This period allows the additive to break down the lead sulfate crystals.
Step 7. Charging
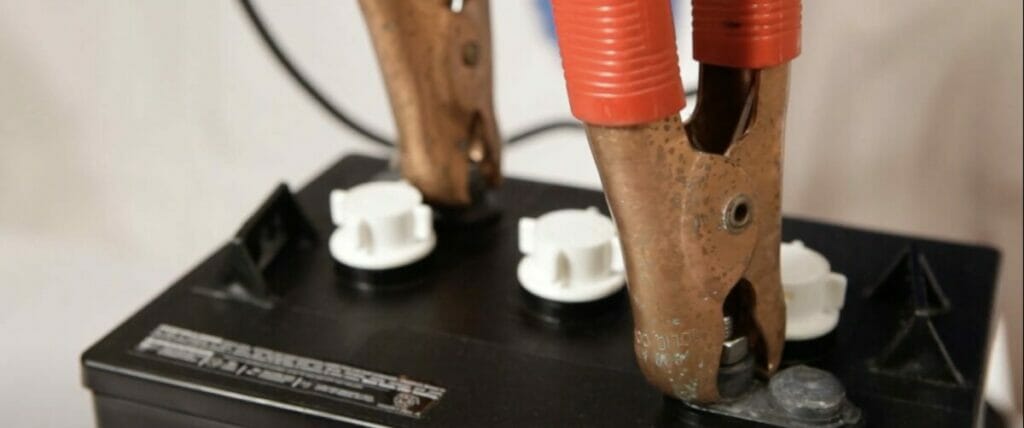

- Recharge the battery using an appropriate charger.
- Follow the standard charging procedure for the specific type of battery, considering factors such as voltage, charge rate, and safety precautions.
Step 8. Evaluation
- Assess the battery’s performance after the chemical treatment and recharge process.
- Observe if there are any improvements in battery capacity, voltage stability, or overall performance.
Frequently Used Tools and Equipment
For safety, I always use gloves and goggles. Battery acid is corrosive, and spills can happen.
Here’s a quick rundown of the tools I used:
- Multimeter
- Battery charger
- Hydrometer
- Gloves and goggles
These are the tools I frequently use when reconditioning batteries. With the right equipment, the tricky task of battery reconditioning can become approachable, even enjoyable. Remember, always put safety first! And don’t forget to have fun with it!
FAQs
How long does reconditioning a battery take?
Reconditioning a battery can take anywhere from 30 minutes to 4 hours, depending on the type and size of the battery. It’s all about patience, my friends! The process might not be as quick as swapping out a battery, but trust me; it’s worth it.
What is the best reconditioning charger?
There are many reconditioning chargers, but I highly recommend the NOCO Genius10. It’s a great charger that can recondition almost any lead-acid battery. It’s user-friendly and efficient, which is a win-win in my book!
Can you recondition batteries at home?
You can recondition batteries in the comfort of your own home! It’s simpler than you might think. You only need a reconditioning charger, safety gear, and a workspace. Just remember always to follow safety guidelines when working with batteries.
Where can I find battery reconditioning services?
If you prefer to leave it to the pros, plenty of battery reconditioning services are available. Local auto shops are a great place to start. When in doubt, search “battery reconditioning near me,” and you’ll find a service that suits your needs.
References
Video References
Justin Miller
LDSreliance
Bradley DePasse
