How Long to Charge a Deep Cycle Battery? (Table & Tips)

A deep cycle battery can be discharged deeply, but how long does it take to charge it?
How long it takes to charge a deep cycle battery depends on its capacity, discharge state, charging current, age, and condition. Usually, it would take 3 to 6 hours if charging at 15 amps, 4.5 to 7.5 hours at 10 amps, 5 to 8.5 hours at 8 amps, and 7.5 to 12.5 hours at 6 amps.
In general, the newer the battery, the smaller its capacity, the lower its discharge, and the higher the charging current, the quicker it will charge. I recommend charging at no more than 15 amps.
Time to Charge a Deep Cycle Battery
How long it takes to charge a deep cycle or any other battery depends on its capacity, discharge state, charging current, and age and condition.
Charge the battery at the right amperage for the right interval for optimum charging. The table below shows the estimated charging time for a deep cycle battery at different amperages for different reserve capacities, assuming the battery is discharged between 60% and 80%. The actual time will depend on the above-mentioned factors.
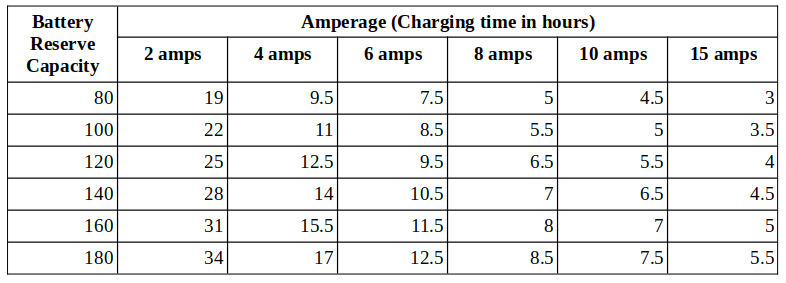
Generally, you can expect the charging time to be shorter than stated if the battery:
- Is discharged less than 60%;
- Is charged at a high current (which should not exceed 15 amps if you want to preserve battery life);
- It is in a new and excellent condition.
To maintain good battery life, I recommend the following:
- Charging a deep cycle battery at low amperage (between 5 and 15 amps) over a longer period;
- To stop charging when the estimated time is reached or if you notice excessive heat, whichever is sooner;
- Charging the battery at least once or twice a week, even if used infrequently;
- Disconnecting the battery when not used for an extended period to minimize draining.
Understanding More About Deep Cycle Batteries
The Basics
Deep cycle batteries are designed to be discharged down as much as 80% time after time and have much thicker plates. They are designed and built differently than automotive and maintenance-free batteries to withstand the rigors of deep discharging and recharging cycles.
Deep cycle refers to the design of these batteries to discharge between 60% and 80% of their capacity, depending on the manufacturer and the construction of the battery. Although these batteries can be cycled down to 20% charge, the best lifespan vs. cost method is to keep the average cycle at about 50% discharge.
How Do Deep Cycle Batteries Work?
Deep cycle batteries provide continuous power over a longer period of time. The power delivery is more consistent and sustained, with a slower release of energy than a starter battery, which delivers quick, high-energy bursts for ignition.
Thicker lead plates with a higher density active material are inside a deep cycle battery. The thicker battery plates resist corrosion through extended charge and discharge cycles.
Applications of Deep Cycle Batteries
Deep cycle batteries are typically used when you need sustained power over a longer period. They’re commonly found in equipment like solar power systems, electric wheelchairs, golf carts, marine applications like electric trolling motors, and recreational vehicles.
In all these examples, the battery is required to provide a steady current over a long period. For example, in a solar power system, the deep cycle battery stores the energy collected by the solar panels during the day, then slowly releases that energy to power lights and appliances in the evening.
In contrast, a car battery is designed to provide a very high current for a very short time to start the car, after which the car’s alternator quickly recharges it. Deep cycle and car batteries are not interchangeable due to these differences in design and purpose.
Types Of Lead Acid Batteries
Various types of deep-cycle batteries exist:
1. Flooded Lead Acid Batteries
Also known as wet cell batteries, these are the most commonly used deep cycle batteries. They have a liquid electrolyte (a mixture of water and sulfuric acid) that floods the battery cells, hence the name. This type requires regular maintenance, which includes checking and refilling the electrolyte level and cleaning any acid spills.
Flooded lead acid batteries usually take longer to charge than other types, but they are typically the least expensive option. They have a lifespan of around 4-8 years, varying depending on their use and maintenance.
2. Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries
AGM batteries have an electrolyte absorbed into a fiberglass mat between the battery plates. This design makes the battery spill-proof and means that AGM batteries don’t require any maintenance. They can be installed at any angle and are more vibration-resistant than flooded batteries.
AGM batteries can charge fairly quickly, up to five times faster than flooded batteries, depending on the charger. Their lifespan is about 3-6 years, but they can sometimes last longer with proper care and usage.
3. Gel Batteries
In Gel batteries, silica is added to the electrolyte, creating a gel-like substance. This makes the batteries spill-proof and vibration resistant, like AGM batteries. However, gel batteries are very sensitive to charging conditions. Charging them too quickly or at too high a voltage can cause permanent damage, requiring a specific type of charger.
Gel batteries tend to be more expensive and have slightly less capacity than AGM or flooded batteries of the same size, but they usually have a longer lifespan, sometimes up to 10 years.
4. Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion deep-cycle batteries are relatively new but offer several advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries. They are much lighter, can be discharged more deeply (up to 100% in some cases), and have a longer lifespan, often up to 10 years or more.
Lithium-ion batteries can also charge much more quickly than lead-acid batteries. However, they are much more expensive initially, although their longer lifespan and improved performance can sometimes offset this cost.
It’s important to note that each type of deep-cycle battery requires a different charging method and voltage, so using a charger compatible with your specific battery type is essential. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific charging guidelines.
References
Solarfam AGM battery. https://www.todoensolar.com/AGM-Solarfam-12V-1500Ah-solar-battery
