Symptoms of a Bad Battery Current Sensor

In this article, I’ll help you correctly identify the symptoms of a bad battery current sensor.
Bad battery current sensor issues can arise occasionally. When the battery current sensor fails, the vehicle might fail to charge properly, resulting in a DTC or a dead battery. Knowing the symptoms can help you to avert further damage to the battery or other parts of the car.
Common symptoms of a bad battery current sensor include:
- Low battery voltage
- Corrosion
- Drift
- Fault indicator
- Inaccurate measurements
- Inconsistent readings
- Weak wiring
- Zero current reading
I will go into more detail below and briefly cover how a bad battery current sensor affects the vehicle and how to confirm it is bad before you decide to remove and replace it.
Symptoms and Signs of a Bad Battery Current Sensor

Here, I’ve covered some symptoms and signs of a bad battery current sensor.
Symptoms
Below are some common symptoms of a possible bad battery current sensor, although you may need to check further to be sure.
- Low battery voltage – The current sensor might give high readings, making the alternator charge the battery less than normal.
- Corrosion on the battery’s terminals could be due to a bad battery current sensor.
- Drift – A drift means that the sensor shows a non-zero current reading even while no current flows. The battery current sensor is unreliable if this happens.
- Fault indicator – see below under definite signs.
- Inaccurate measurement – The battery current sensor consistently fails to measure the charging and discharging rates accurately. You can check to see if they deviate from the actual values.
- Inconsistent readings – If the battery current sensor’s reading fluctuates or is discontinuous, it may not function properly.
- Wiring – A weak or broken wire on the sensor could cause the battery current sensor not to work normally. If so, you might only need to replace the wire.
- A zero current reading may be due to a failed battery current sensor, a loose connection, or weak wiring.
A problem with other vehicle components, such as the battery or alternator, could also be due to a bad battery current sensor. It could also happen that a fault elsewhere causes the battery current sensor to behave erratically, so you should rule them out before suspecting the battery current sensor.
Definite Signs
Many vehicles give a visual indication of a bad battery current sensor on the dashboard, and you can check the resistance between the pins to confirm.
A faulty battery current sensor usually causes the Charging System Indicator (CSI) to display an error code. For example, several Accord, Fit, and HR-V models will give the trouble code (DTC) P154A, according to Honda bulletin 16-026. In some Acura vehicles, the code of a faulty battery sensor can also cause P154A. The code may vary in other vehicles and models.
Regardless, the battery sensor should be replaced if the error code appears or the resistance test confirms the same.
PCM-Controlled Charging Systems
In a PCM-controlled charging system, the PCM monitors the battery current sensor, making it easier to know when it goes bad. (Erjavec & Thompson, 2020)
It also monitors the battery’s voltage and temperature to determine its SOC. The battery current sensor, in this case, is typically a 3-wire Hall-effect sensor that feeds information directly into the PCM.
Battery Current Sensor Issues
A battery current sensor is a sensitive instrument vulnerable to dirt and moisture exposure and can be damaged from battery acid contamination.
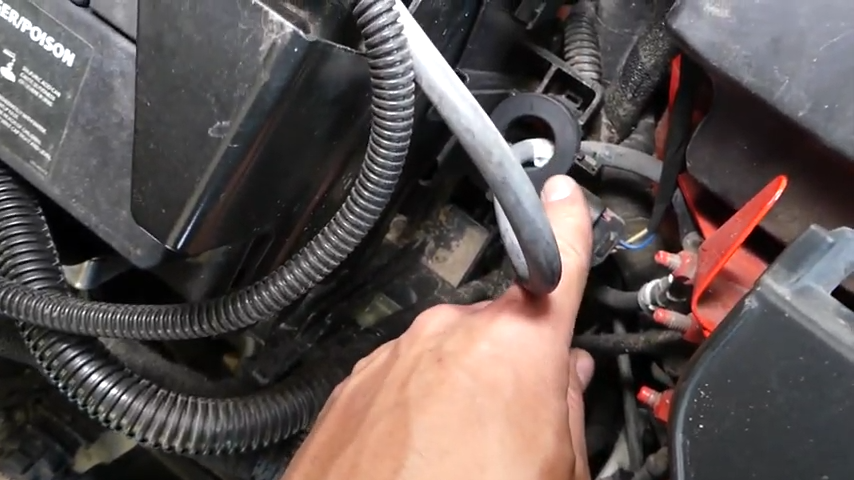

Sensitivity
A battery sensor is a delicate device that can get damaged during battery servicing or removal.
The sensitivity requires handling it very carefully. Honda once issued a recall (service bulletins 17-057 and 17-069) to inspect and, if necessary, replace the battery management sensor in Honda Accord models from 2013 to 2016, except the hybrid ones.
Dirt, Moisture, and Battery Acid Contamination
Dirt, moisture, or battery acid can enter a battery current sensor and shorten or damage it.
In some BMW vehicles, for example, the battery is located in the trunk’s side compartment, and water leaking into the battery can damage the sensor, which IBM calls an “Intelligent Battery Sensor” (IBS).
A failed IBS has been linked to several electrical issues, including the failure of the vehicle to start. Moisture and road salt getting into the sensor, according to bulletin 17-069, “could result in an electrical short and, consequently, a fire.”
Current Bypass
Suppose a car has a battery current sensor and additional electrical accessories connected directly to the battery’s negative terminal.
In that case, the electric current will bypass the battery current sensor, resulting in inaccurate readings. To ensure proper operation of the battery management system, the owner’s manual for the 2019 Ford Explorer recommends not connecting electrical devices’ ground connection directly to the low voltage battery negative post (BMS).
A faulty battery sensor in many vehicles can render the Stop/Start system inoperable.
More About Battery Current Sensors
Here, I’ve briefly covered more information about battery current sensors for interested readers.
Battery sensors are recent sensors that have replaced manual battery maintenance processes. They cater to the increased demand for electrical functions.
If you’re driving an old car without battery current sensors, it’s time to replace it.
Location and Operation
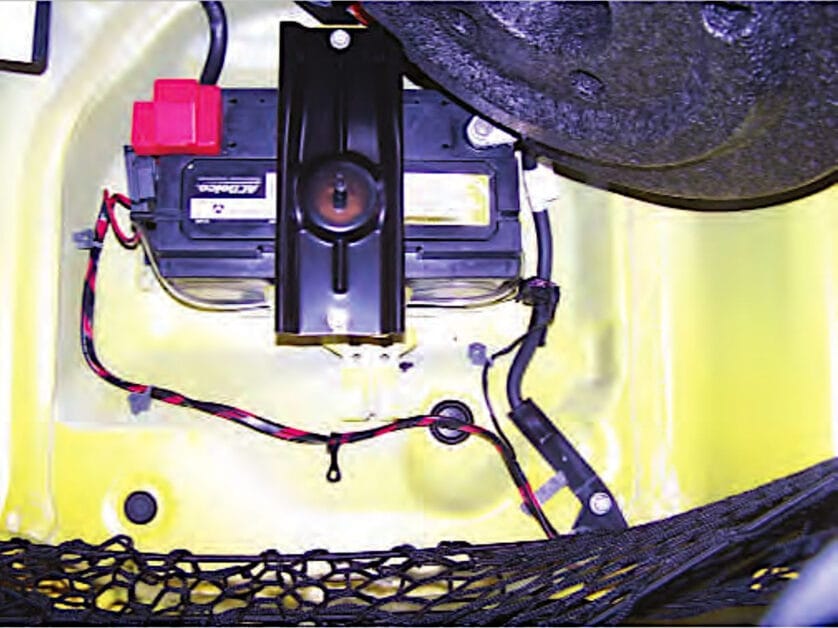
The battery current sensor is located at the terminal clamp and secured to the car frame with screws.
It is connected to the battery’s negative cable. Battery sensors are linked to the car’s computer and display a warning light if there is a discrepancy.
A shunt in the sensor measures current and temperature, essential parameters for a car’s computer. BZE algorithms in a car computer use these signals to detect the battery’s health, state of charge, and function.
Here, health, charge, and functions stand for:
- Battery health refers to a battery’s ability to store and supply current.
- The state of Charge specifies the amount of charge remaining in the battery. The amount of charge left determines fuel efficiency and current usage.
- State function predicts the relationship between a voltage curve and a load profile.
Replacing a Bad Battery Current Sensor
The battery sensor is inexpensive to replace.
A mechanic may charge $50-$210 for the part, plus $35-$110 for labor. In some vehicles, a battery sensor is included with the battery cable. The toughest part is correctly diagnosing the problem, which is not always easy.
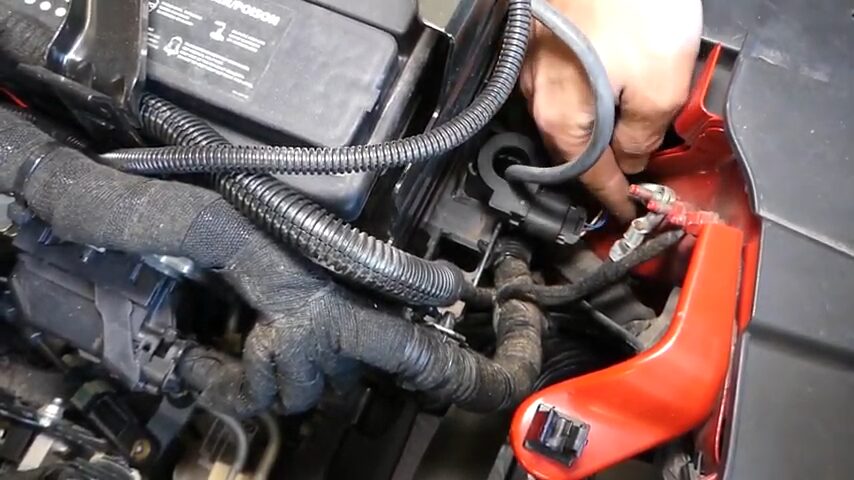

The following precautions must be taken when changing a battery current sensor:
- Remember that battery current sensors are delicate and can be permanently damaged if installed wrongly.
- Reading the user’s manual is critical because each car battery management system operates differently.
- It is advised to seek professional assistance when replacing the battery current sensor.
References
Website Resources:
- fuel efficiency. https://www.caranddriver.com/research/a32780283/fuel-efficiency/
- old car. https://www.nationwide.com/lc/resources/auto-insurance/articles/how-old-is-a-classic-car
Books:
- Automotive Technology: A systems approach. 7th Edition. Cengage Learning. 2019. https://au.cengage.com/c/isbn/9781337794213/?filterBy=Higher-Education
- Erjavec, Jack & Rob Thompson. Automotive technology: A systems approach. 7th edition. 2020. https://www.gettextbooks.com/author/Rob_Erjavec_Thompson
Video References:
Let’s Kill Sum Time
Auto Repair Guys
