How to Test Spark Plug Wires without a Multimeter
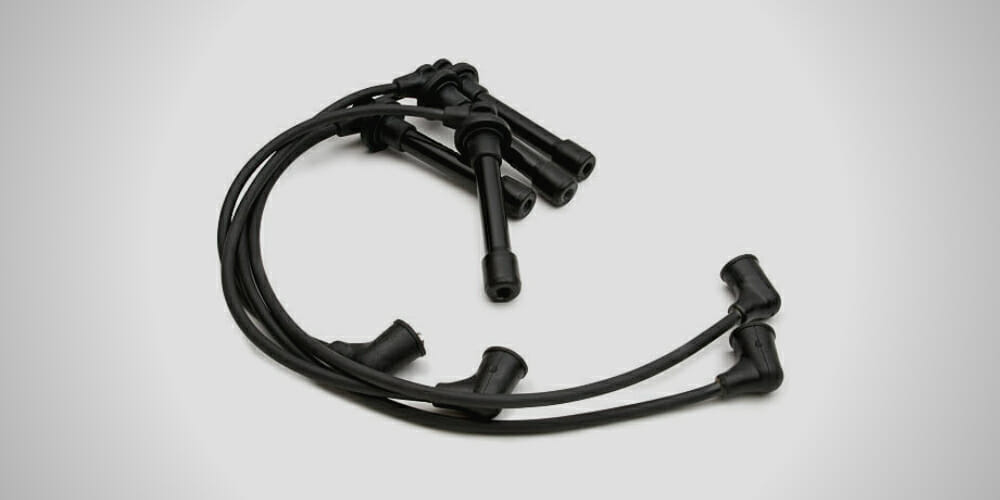

Spark plug wires transmit thousands of volts to the spark plugs up to 45,000V, depending on the requirements. They have strong insulation and a rubber boot on each end to avoid excessive voltages from leaping off the wire before it touches the spark plug.
In general, here’s how to test spark plug wires without a multimeter:
- Turn off the car engine and check the spark plug wires.
- Perform an inspection with the car engine running.
- Verify to make sure your spark plug wires are correctly routed.
Spark plug wires operate in a tough environment, and they can break at any time, exposing the spark plugs to a poor or no spark at all. Thus, learning how to quickly test with spark plug wires will be worthwhile, especially without the need for multimeters.
Step #1: Turn Off the Engine and Examine the Spark Plug Wires
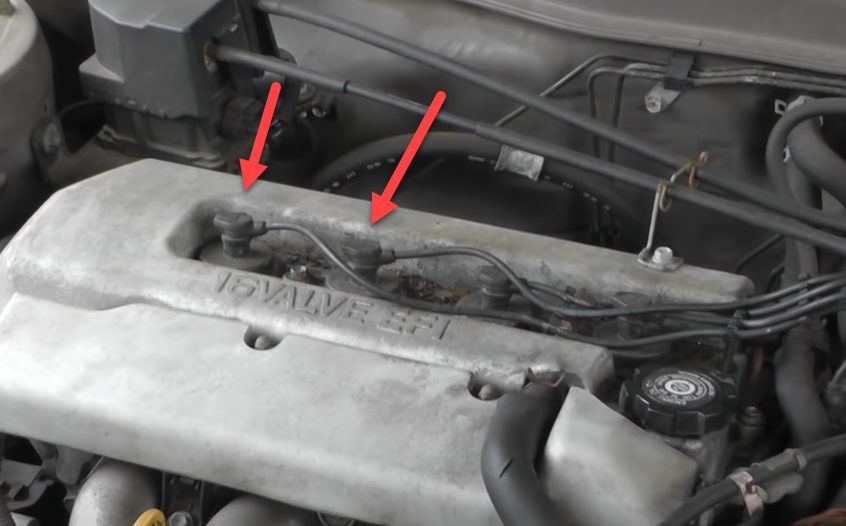

- Examine the wires or boots for physical damage such as scratches or burn marks. Examine the spark plug wires and the cover on top of them, known as the boot, with a flashlight or well-lit environment. These will be a series of wires that run from the cylinder head to the distributors or ignition coils on the other end. As the wires move away from the spark plugs, look at the insulation around them. (1)
- Inspect the area between the boot and the spark plug and coil for rust. Loosen the spark plug’s top boot and inspect where the contact is established. Examine for any discoloration or deterioration. Carefully detach the spark plug and look for corrosion or scratches on the bottom.
- Check the spring clips in the distributor cover that hold the wires in place. Trace the wires down from the cylinder head to where they connect to the distributor on the other end. Wiggle the wire’s end to ensure that the clips are securely fastened to the top of the spark plug. They produce the pressure that maintains the wire and plug attached firmly when they are not broken.
Step #2: Perform an Inspection with the Engine Running

Power up the engine and check for electrical arcs around the wires or cracking noise, indicating a high-voltage electrical leak. Avoid touching the wires while the engine is running due to the high voltage’s risk of electrical shocks.
While you’re looking at it, get someone else to rev the engine. Look for unusual changes, such as sparks or smoke, and listen to them.
Now, consider the signs and symptoms of a defective spark plug wire. Faulty spark plug wire has telltale symptoms of wear and tear. The most prevalent signs and symptoms are:
- A random idle
- Engine failure
- Interference with radio
- Reduced fuel mileage.
- Emissions tests failed to owe to high hydrocarbon emissions or a fault code suggesting cylinder misfire. (2)
- Inspect engine light
You may also look for arcing by spraying the spark plug wires. Fill a spray bottle halfway with water and spray the wires all over. To see whether any sparking happens, concentrate your spray on the boots that connect to the spark plugs. Power off the engine and examine the boots further if you discover arcing around the spark plug.
Step #3: Using a Diagram to Check the Wires
Inspect to see if your spark plug wires are appropriately routed. See the vehicle’s manual’s spark plug diagram to assist you with this task. Follow each spark plug wire from its engine block connections to its appropriate spark plug. Each wire must be attached to a distinct spark plug.
This could be a complication if you replaced your spark plugs before, especially if the boots’ position is incorrect. Cross-coupling can cause an energy drain, which can lead to engine problems.
Helpful Tips
- Even though your spark wires have a boot, some engines utilize coil-on-plug (COP) setups that totally ignore the spark plug wires.
- To prevent conduction, drain and maintain the spark plug wires neat.
- Crossing spark plug wires are not necessarily a bad thing. Some manufacturers do this to neutralize magnetic fields.
FAQs
What causes the spark plug wire damage?
1. Engine Vibration: It can cause the electrical contacts at the spark plugs to slip. The ignition coil and spark plug wires may be damaged if the spark plugs require greater voltage to ignite.
2. Engine Block Heat: High engine heat can cause wire insulation to melt, causing the voltage to jump to the ground rather than entering the spark plugs.
What occurs if my spark plug wire breaks?
If your spark plug wires are damaged, you may encounter the following symptoms:
– Engine failure
– Rusty idling
– Failed emissions tests
– Having trouble starting your car
– The Check Engine Light (CEL) is illuminated
These indications, however, could signal the breakdown of other engine components.
Take a look at some of our related articles below.
- How to test spark plug with multimeter
- How to test ignition coil with multimeter
- How to use a multimeter to test voltage of live wires
References
(1) environment – https://www.britannica.com/science/environment
(2) hydrocarbon emissions – https://www.statista.com/statistics/1051049/
china-amount-hydrocarbon-emission-by-type-of-vehicle/
